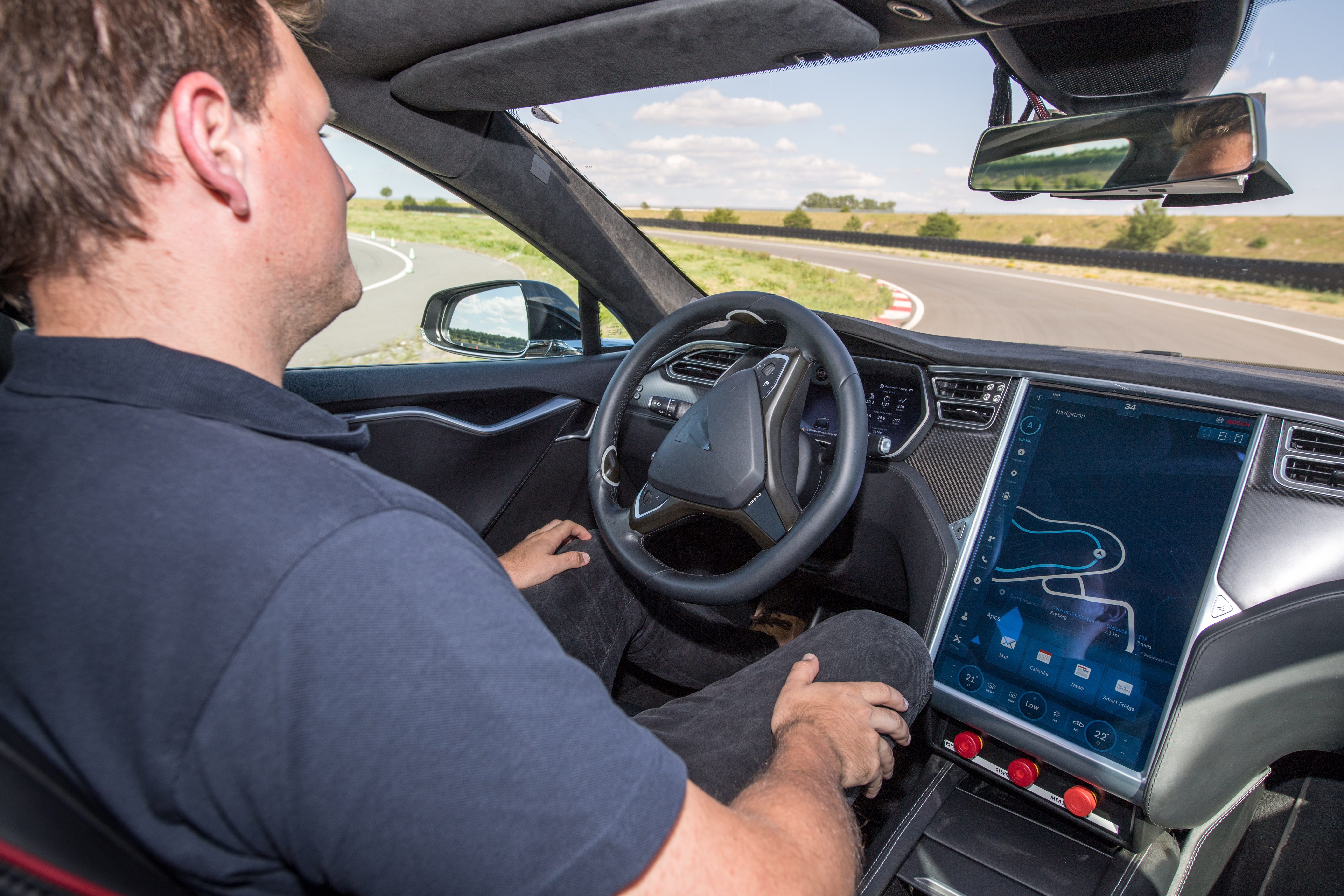
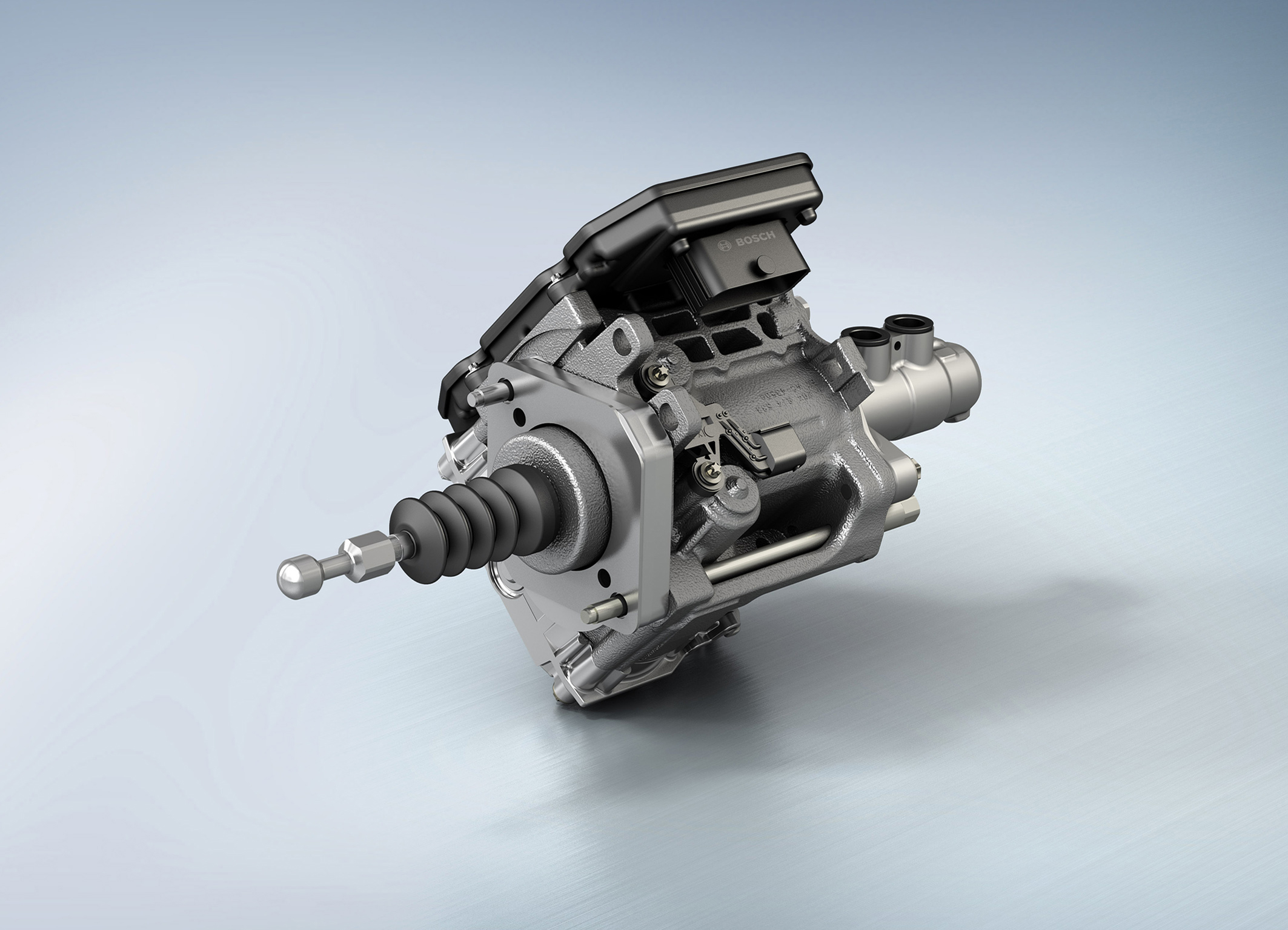
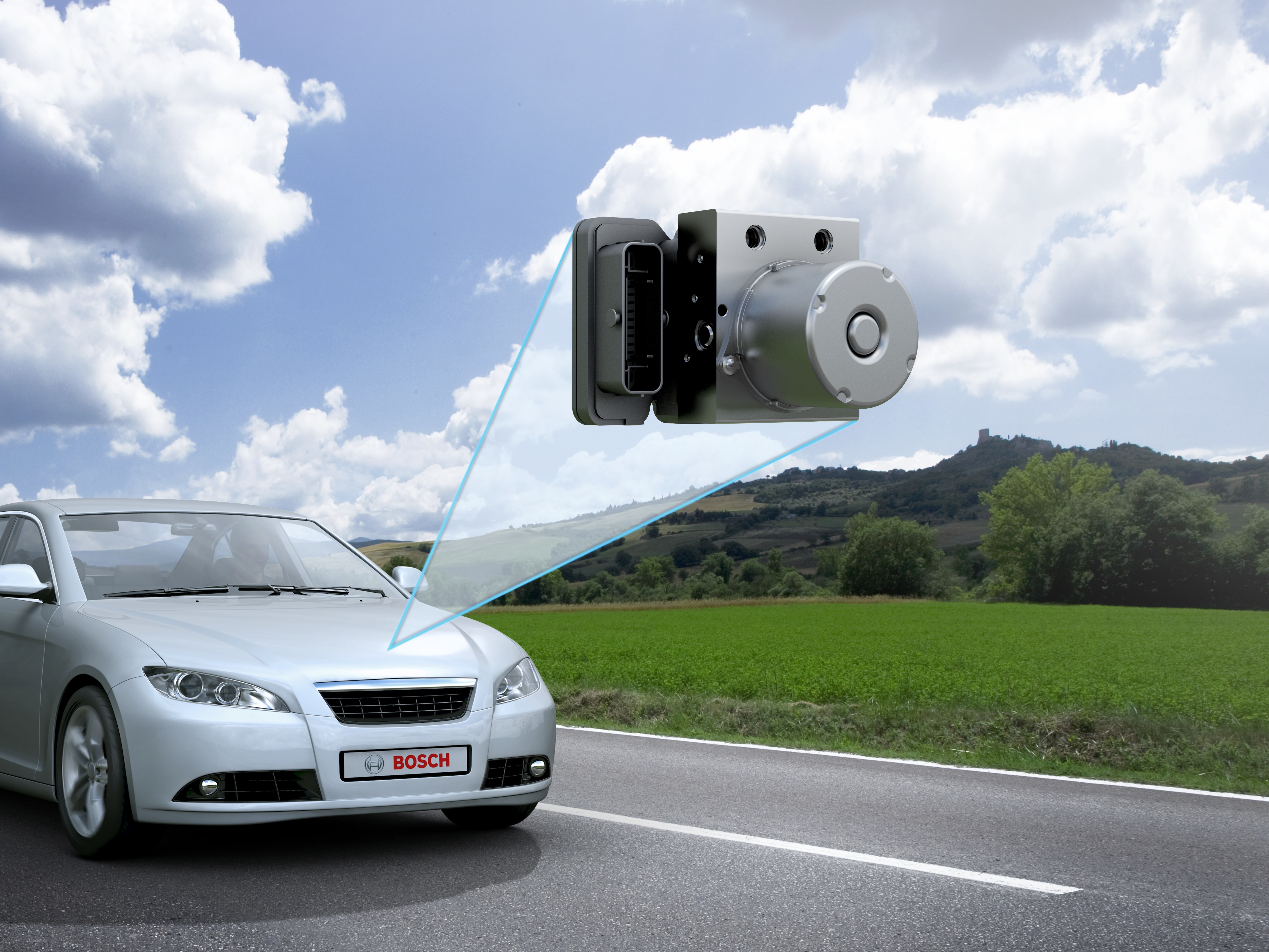
DETROIT – Without redundancy, there is no automated driving. The promise of automated driving requires a mix of technological, societal and regulatory development and cooperation. The technology continues to advance thanks to sensors and software, but also thanks to redundancy. In order to realize fully-automated driving on the path to the accident-free future, redundancy in safety-critical systems such as braking and steering is an absolute.
EXPERIENCE BOSCH AT NAIAS 2018 in Detroit, Michigan, USA:
At NAIAS 2018, Bosch is presenting automated, connected and electrified technologies with a focus on how vehicle electrification is becoming more desired and accessible.
BOSCH BOOTH: Monday to Thursday, January 15-18, 2018,
on Level Three, Room 330A, Cobo Center.
Mobility is the largest Bosch Group business sector. According to preliminary figures, it generated sales of 55.9 billion euros in 2024, and thus contributed around 62 percent of total sales. This makes the Bosch Group one of the leading mobility suppliers. Bosch Mobility pursues a vision of mobility that is safe, sustainable, and exciting. For its customers, the outcome is integrated mobility solutions. The business sector’s main areas of activity are electrification, software and services, semiconductors and sensors, vehicle computers, advanced driver assistance systems, systems for vehicle dynamics control, repair-shop concepts, as well as technology and services for the automotive aftermarket. Bosch is synonymous with important automotive innovations, such as electronic engine management, the ESP anti-skid system, and common-rail diesel technology.
The Bosch Group is a leading global supplier of technology and services. It employs roughly 417,900 associates worldwide (as of December 31, 2024). According to preliminary figures, the company generated sales of 90.5 billion euros in 2024. Its operations are divided into four business sectors: Mobility, Industrial Technology, Consumer Goods, and Energy and Building Technology. With its business activities, the company aims to use technology to help shape universal trends such as automation, electrification, digitalization, connectivity, and an orientation to sustainability. In this context, Bosch’s broad diversification across regions and industries strengthens its innovativeness and robustness. Bosch uses its proven expertise in sensor technology, software, and services to offer customers cross-domain solutions from a single source. It also applies its expertise in connectivity and artificial intelligence in order to develop and manufacture user-friendly, sustainable products. With technology that is “Invented for life,” Bosch wants to help improve quality of life and conserve natural resources. The Bosch Group comprises Robert Bosch GmbH and its roughly 470 subsidiary and regional companies in over 60 countries. Including sales and service partners, Bosch’s global manufacturing, engineering, and sales network covers nearly every country in the world. Bosch’s innovative strength is key to the company’s further development. At 136 locations across the globe, Bosch employs some 86,900 associates in research and development, of which nearly 48,000 are software engineers.
Additional information is available online at www.bosch.com, www.iot.bosch.com, www.bosch-press.com.