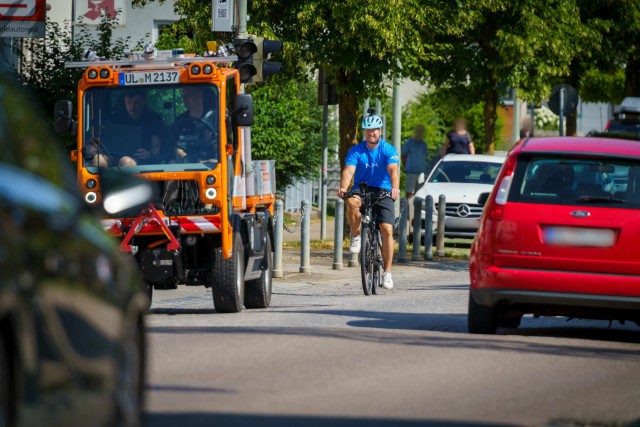
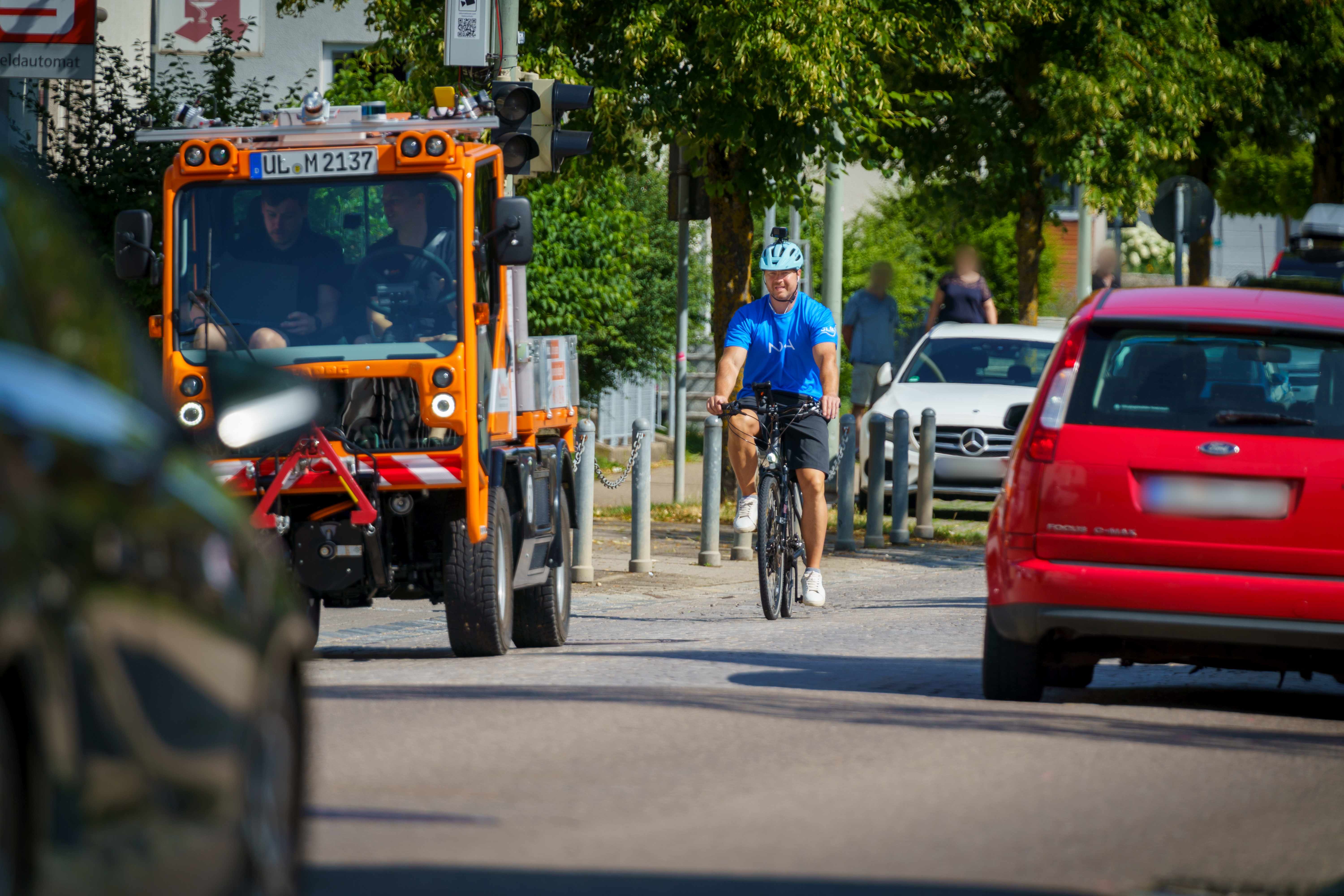
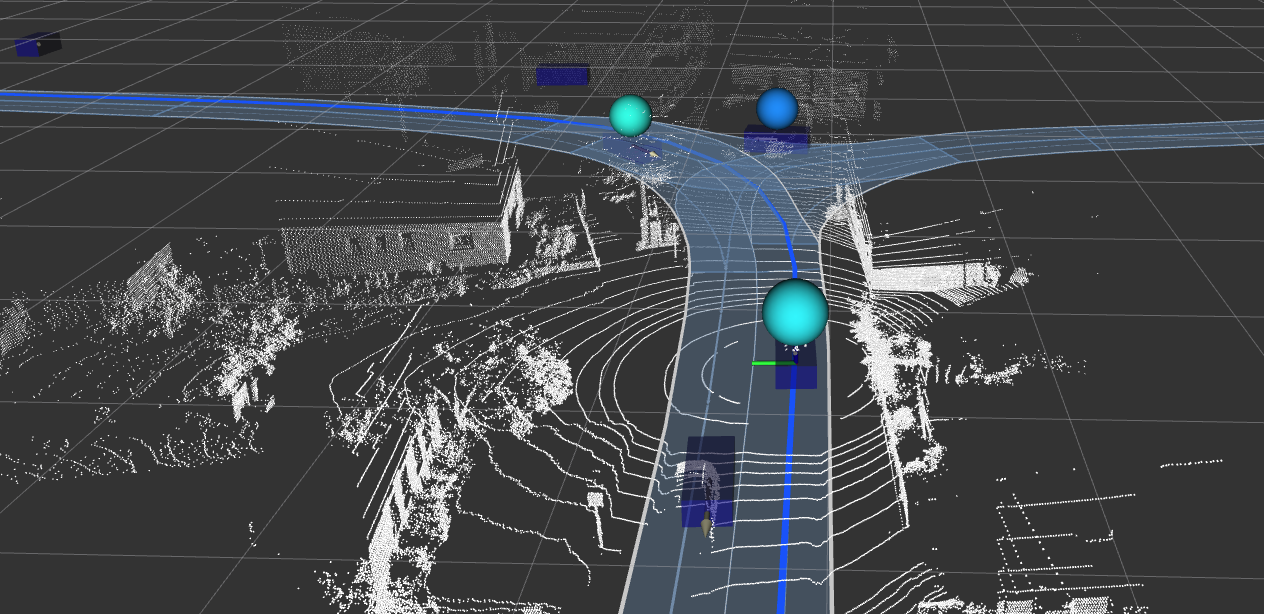
Stuttgart, Germany – The digital transformation, increasing urbanization and automation, as well as the need for greater energy efficiency and climate action are tough challenges currently facing the mobility sector. In the three-year LUKAS research project, Bosch, InMach, IT-Designers, Mercedes-Benz, Nokia, Ulm University, and the University of Duisburg-Essen are researching how to improve traffic efficiency and safety in future mixed traffic scenarios of urban traffic environments. LUKAS is the abbreviation of the German name "Lokales Umfeldmodell für das kooperative, automatisierte Fahren in komplexen Verkehrssituationen” (local environment model for cooperative automated driving in complex traffic situations). Reliable communication between automated and non-automated traffic participants as well as within the infrastructure plays a key role here. The project was funded by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK) with 5.2 million euros as part of its program for new vehicle and systems technology.
Contact person for press inquiries:
Jennifer Kallweit,
Phone: +49 711 811-42239
E-mail: jennifer.kallweit@de.bosch.com
About Bosch
The Bosch Group is a leading global supplier of technology and services. It employs roughly 417,900 associates worldwide (as of December 31, 2024). According to preliminary figures, the company generated sales of 90.5 billion euros in 2024. Its operations are divided into four business sectors: Mobility, Industrial Technology, Consumer Goods, and Energy and Building Technology. With its business activities, the company aims to use technology to help shape universal trends such as automation, electrification, digitalization, connectivity, and an orientation to sustainability. In this context, Bosch’s broad diversification across regions and industries strengthens its innovativeness and robustness. Bosch uses its proven expertise in sensor technology, software, and services to offer customers cross-domain solutions from a single source. It also applies its expertise in connectivity and artificial intelligence in order to develop and manufacture user-friendly, sustainable products. With technology that is “Invented for life,” Bosch wants to help improve quality of life and conserve natural resources. The Bosch Group comprises Robert Bosch GmbH and its roughly 470 subsidiary and regional companies in over 60 countries. Including sales and service partners, Bosch’s global manufacturing, engineering, and sales network covers nearly every country in the world. Bosch’s innovative strength is key to the company’s further development. At 136 locations across the globe, Bosch employs some 86,900 associates in research and development, of which nearly 48,000 are software engineers.
The company was set up in Stuttgart in 1886 by Robert Bosch (1861–1942) as “Workshop for Precision Mechanics and Electrical Engineering.” The special ownership structure of Robert Bosch GmbH guarantees the entrepreneurial freedom of the Bosch Group, making it possible for the company to plan over the long term and to undertake significant upfront investments in the safeguarding of its future. Ninety-four percent of the share capital of Robert Bosch GmbH is held by Robert Bosch Stiftung GmbH, a charitable foundation. The remaining shares are held by Robert Bosch GmbH and by a corporation owned by the Bosch family. The majority of voting rights are held by Robert Bosch Industrietreuhand KG. It is entrusted with the task of safeguarding the company’s long-term existence and in particular its financial independence – in line with the mission handed down in the will of the company’s founder, Robert Bosch.
Additional information is available online at www.bosch.com, www.iot.bosch.com, www.bosch-press.com.